Color management provides for uniform color rendering on computer systems. All input devices (scanners, digital cameras, etc.), the computer and all the programs running on it and the output devices (monitors, printers, video projectors) should be able to detect and display color information uniformly. Due to the different technology used in these devices they differ greatly in their capability of detecting and displaying color information. This capability is defined by color spaces, also called gamut. A printer, for example, uses a different color space compared to a monitor and a video projector again a different one. Color management acts as an intermediary between these different color spaces.
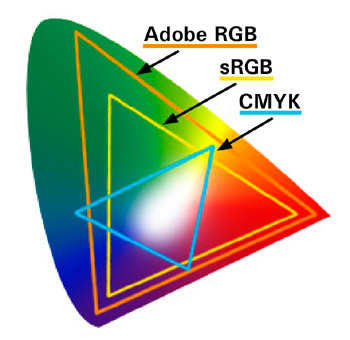
For the computer colors are only figures and there are no such technological limits as there are for input and output devices. The only important thing is that you need to decide on one particular color space. In the world of PCs, the Internet and HDTV the standard color space is sRGB IEC61966-2.1. As this color space has become too small for superior image editing and the detailed display of color shades other color spaces were defined as well, e.g. Adobe RGB 1998 or Apple RGB, to name just a few.

But how can we achieve uniform color rendering? It seems only too logical that a printer with its CMYK print color range cannot print all colors that can be displayed in the RGB color space. Color management uses color profiles to convert RGB colors into CMYK colors that are as close to RGB color rendering as possible. Ideally, every input and output device has an individual color profile for accurate color rendering. And if you use a different sort of paper or ink for your printer you actually need a new color profile so to say.
An important fact is that the media files are to be saved and archived in a sufficiently large color space. The aim is to produce as "output-neutral" media files as possible, which in combination with color profiles, can be prepared and used for output by a number of different devices and still achieve optimum results. Even if your device is not yet capable of printing or projecting all the available color shades – the future will bring new and advanced technology which will be able to do so. Therefore it would be definitely a bad idea to archive an image in a CMYK color space, as it is smaller than a RGB color space and is only useful for printing. Monitors, displays and video projectors always produce images in accordance with RGB color space. In their color palette they correspond more or less to sRGB color space, which actually corresponds to HDTV color space. Good monitors and video projectors, however, have a much greater color space than sRGB and definitely require a color profile for correct color rendering.
Unfortunately, color management as explained above cannot be applied to videos. HD videos are usually saved in color space ITU BT Rec 709 which corresponds to sRGB. Cinema films are an exception as they use the much larger color space DCI-XYZ. If both HD videos and images are to be used in a show it may be useful to calibrate the output equipment to sRGB and to output the show in this color space.
Wings Vioso RX can prepare for output to any color space require, i.e. convert the picture color space to the output device color space. Under Global Options - Color management you can define the corresponding color space by entering a color profile. If you have no color profile available for your output device you can used the standardized color space sRGB IEC1966-2.1/HDTV. For color conversion there are two methods available:
During display data creation images are converted from the document color space to the output color space. Since this is done before the presentation it saves performance but calls for a recreation of display data as soon as a different monitor or video projector is used. Wings Vioso RX, however, supports several display data sets. If you have created display data with the corresponding color profile for your monitor or video projector you can change over between these profiles without having to create new display data.
Images are only converted to the output device's color space during playback. This uses up extra system resources but the advantage is that the output device can be exchanged at any time.
It is clear that all pictures should have an embedded color profile, otherwise accurate color rendering is not possible. Therefore, the use of a color profile must be enabled in the Options. Important: Wings Vioso RX can only read color profiles in JPG- and TIF-format! Tip: If restricted memory capacity is no major issue, you should use TIF format for the pictures,  Advantages of the TIF format.
Advantages of the TIF format.
When videos are rendered the picture display data is always converted to sRGB to make it compatible with the video color space BT.709.
For superior image editing and presentation of AV shows you can calibrate your output devices, i.e. monitors and video projectors. A measuring instrument compares the displayed colors with standard values and prepares a color profile containing the color correction values. This color profile is passed on to the graphics card which corrects color rendering for the corresponding device. If you have no measuring units for fine calibration of input and output devices you can have calibration and profiling also performed as a service by an expert.
The color profile for the device is usually assigned via color management tools or in Windows under Control Panel - Color Management and changes the settings for the graphics card or, in the case of hardware-calibrated monitors, for the device itself. Here, Whitepoint and Gamma are directly influenced. If, for presentation in Wings Vioso RX, the color profile is to become effective for the color space conversion of images that are not saved in sRGB color space this needs to be defined in the color management options. See Global Options - Color Management.